Assinaturas em anel
Assinaturas em anel na criptografia, é um tipo de assinatura digital que pode ser executada por qualquer membro de um grupo de usuários que tenha chaves. Portanto, uma mensagem assinada com uma assinatura de anel é endossada por alguém em um grupo específico de pessoas. Uma das propriedades de segurança de uma assinatura de anel é que deve ser computacionalmente inviável determinar quais das chaves dos membros do grupo foram usadas para produzir a assinatura. Foi inventada por Ronald Rivest, Adi Shamir e Yael Tauman, e introduzidas no Asiacrypt.[1] O nome, assinatura em anel, vem da estrutura em forma de anel do algoritmo de assinatura.
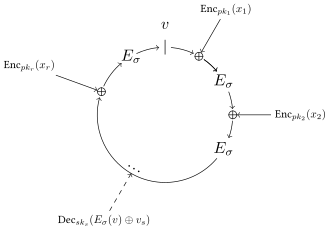
Aqui está uma implementação em Python do artigo original usando o RSA:
import os, hashlib, random, Crypto.PublicKey.RSA
class ring:
def __init__(self, k, L=1024):
self.k = k
self.l = L
self.n = len(k)
self.q = 1 << (L - 1)
def sign(self, m, z):
self.permut(m)
s = [None] * self.n
u = random.randint(0, self.q)
c = v = self.E(u)
for i in (range(z+1, self.n) + range(z)):
s[i] = random.randint(0, self.q)
e = self.g(s[i], self.k[i].e, self.k[i].n)
v = self.E(v^e)
if (i+1) % self.n == 0:
c = v
s[z] = self.g(v^u, self.k[z].d, self.k[z].n)
return [c] + s
def verify(self, m, X):
self.permut(m)
def _f(i):
return self.g(X[i+1], self.k[i].e, self.k[i].n)
y = map(_f, range(len(X)-1))
def _g(x, i):
return self.E(x^y[i])
r = reduce(_g, range(self.n), X[0])
return r == X[0]
def permut(self, m):
self.p = int(hashlib.sha1('%s' % m).hexdigest(),16)
def E(self, x):
msg = '%s%s' % (x, self.p)
return int(hashlib.sha1(msg).hexdigest(), 16)
def g(self, x, e, n):
q, r = divmod(x, n)
if ((q + 1) * n) <= ((1 << self.l) - 1):
rslt = q * n + pow(r, e, n)
else:
rslt = x
return rslt
Para assinar e verificar duas mensagens em um anel de quatro usuários::
size = 4
msg1, msg2 = 'hello', 'world!'
def _rn(_):
return Crypto.PublicKey.RSA.generate(1024, os.urandom)
key = map(_rn, range(size))
r = ring(key)
for i in range(size):
s1 = r.sign(msg1, i)
s2 = r.sign(msg2, i)
assert r.verify(msg1, s1) and r.verify(msg2, s2) and not r.verify(msg1, s2)
Referências
- How to leak a secret, Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Yael Tauman, ASIACRYPT 2001. Volume 2248 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 552–565.