Fenoperidina
Fenoperidina (Operidine ou Lealgin), é um opioide usado como um anestésico geral.
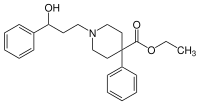 | |
Fenoperidina | |
| Nome IUPAC (sistemática) | |
| ethyl 1-(3-hydroxy-3-phenylpropyl)-4-phenylpiperidine-4-carboxylate | |
| Identificadores | |
| CAS | 562-26-5 |
| ATC | N01AH04 |
| PubChem | 11226 |
| ChemSpider | |
| Informação química | |
| Fórmula molecular | C23H29NO3 |
| Massa molar | 367.481 |
| SMILES | OC(C1=CC=CC=C1)CCN(CC2)CCC2(C3=CC=CC=C3)OC(CC)=O |
| Farmacocinética | |
| Biodisponibilidade | ? |
| Metabolismo | ? |
| Meia-vida | ? |
| Excreção | ? |
| Considerações terapêuticas | |
| Administração | ? |
| DL50 | ? |
Uso médico
Fenoperidina é um analgésico opioide -- analgésico narcótico.[1][2][3]
Referências
- Pinaud M, Desjars P, Nicolas F.; Hemodynamic effects of equipotent doses of phenoperidine and fentanyl in man; Anesth Analg (Paris). 1978 May-Jun;35(3):453-63.
- Jeffrey K. Aronson; Meyler's Side Effects of Drugs: The International Encyclopedia of Adverse Drug Reactions and Interactions; Elsevier, 2015. pg 693
- Enno Freye; Opioids in Medicine: A Comprehensive Review on the Mode of Action and the Use of Analgesics in Different Clinical Pain States; Springer Science & Business Media, 2008.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.