Holoártico
Holoártico ou Holártico (do grego: holos "todo" e arktikos "urso") é a designação usada em biogeografia para referir conjuntamente os habitats encontrados nos continentes boreais da Terra. A região biogeográfica holoártica assim criada é em geral dividida na ecozona paleártica, que inclui o norte de África e toda a Eurásia, com excepção do sueste asiático e o subcontinente indiano, e na ecozona Neártica, que compreende toda a América do Norte até ao sul do México. Em geobotânica esta região corresponde, grosso modo, ao Reino Boreal.
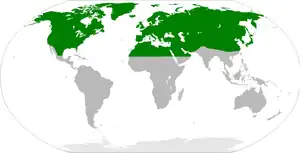
Região holoártica.
Notas
Referências
- Bennet, K. D.; J. H. Lawton; A. Gibbs; M. H. Williamson; M. W. Holdgate; W. D. Hamilton; G. R. Conway. 1986. The Rate of Spread and Population in Increase of Forest Trees During the Postglacial [and Discussion]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences 314:1167:523-531.
- Rodriguez, J;J. Hortal.;M. Nieto. 2006. An evaluation of the influence of environment and biogeography on community structure: the case of Holarctic mammals. Journal of Biogeography Vol. 33:2:291-303.
- Williams, D. W.; A. M. Liebhold. 2002. Climate change and the outbreak ranges of two North American bark beetles. Agricultural and Forest Entomology 4:2:87–99.
- Taberlet, P.; R. Cheddadi 2002. Quaternary Refugia and Persistence of Biodiversity (in Science's Compass; Perspectives). Science, New Series 297:5589:2009-2010.
- Coope, G. R.; A. S. Wilkins. 1994. The Response of Insect Faunas to Glacial-Interglacial Climatic Fluctuations [and Discussion] (in Historical Perspective). Philosophical Transactions: Biological Sciences 344:1307:19-26.
- Logan, J. A.; J. Régnière; J. A. Powell. 2003. Assessing the Impacts of Global Warming on Forest Pest Dynamics (in Reviews). Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 1:3:130-137.
- Paquet, P. C.; R. F. Noss; H. B. Quigley; M. G. Hornocker; T. Merrill. 1996. Conservation Biology and Carnivore Conservation in the Rocky Mountains (in Special Section: Large Carnivore Conservation in the Rocky Mountains of the United States and Canada). Conservation Biology 10:4:949-963.
- Stewart, J.R.; A.M. Lister. 2001. Cryptic northern refugia and the origins of the modern biota. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 16:11:608-613.
- Stokstad, E. 2004. Defrosting the Carbon Freezer of the North. Science 304:5677:1618-1620.
- Sommer, R. S.; N. Benecke. 2005. The recolonization of Europe by brown bears Ursus arctos Linnaeus, 1758 after the Last Glacial Maximum. Mammal Review 35:2:156-164.
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. Disponible en: http://unfccc.int/2860.php. Consultado en diciembre de 2007.
- Yellowstone to Yukon Conservation Initiative. Actualizado en 2006. Disponible en http://www.y2y.net. Accessed December 2007.
- Schultz, J. 2007. The Ecozones of the World. Traducido al inglés por B. Ahnert. Segunda Edición. Springer, Verlag, Netherlands.
Ver também
Ligações externas
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.