Ácido gama-amino-beta-hidroxibutírico
Ácido gama-amino-beta-hidroxibutírico (GABOB, do inglês: gamma-Amino-beta-hydroxybutyric acid), também conhecido como gamibetal ou buxamin, é um derivado do neurotransmissor GABA. É encontrado naturalmente no corpo humano mas não se sabe se ele tem um papel fisiológico importante em concentrações normais.
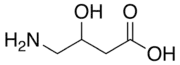 | |
Ácido gama-amino-beta-hidroxibutírico | |
| Nome IUPAC (sistemática) | |
| 4-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid | |
| Identificadores | |
| CAS | 352-21-6 |
| ATC | ? |
| PubChem | 2149 |
| ChemSpider | |
| Informação química | |
| Fórmula molecular | C4H9NO3 |
| Massa molar | 119,12 g/mol |
| Farmacocinética | |
| Biodisponibilidade | ? |
| Metabolismo | Nenhum |
| Meia-vida | ? |
| Excreção | ? |
| Considerações terapêuticas | |
| Administração | ? |
| DL50 | ? |
O GABOB tem propriedades anticonvulsivas,[1] mas é de potência relativamente baixa, quando utilizado por si só, e é mais útil como um tratamento adjuvante usado juntamente com outra droga anticonvulsivante.[2] Tem dois estereoisômeros, com o isômero (3S) d-GABOB sendo aproximadamente duas vezes mais potente como anticonvulsivo que o isômero (3R) l-GABOB.[3]
Referências
- Chemello R, Giaretta D, Pellegrini A, Testa G (julho–agosto de 1980). «Effect of gamma-amino-beta-hydroxybutyric acid (GABHB) on experimentally-induced epileptic activity. (Italian)». Rivista di Neurologia. 50 (4): 253–268. PMID 7466221
- García-Flores E, Farías R. (1997). «Gamma-Amino-beta-hydroxybutyric acid as add-on therapy in adult patients with severe focal epilepsy». Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery. 69(1–4 Pt 2): 243–236. PMID 9711762
- Roberts E, Krause DN, Wong E, Mori A (Fev. 1981). «Different efficacies of d- and l-gamma-amino-beta-hydroxybutyric acids in GABA receptor and transport test systems» (pdf). Journal of Neuroscience. 1 (2): 132–140. PMID 6267220
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.